Comparative Visual Analytics for Assessing Medical Records with Sequence Embedding
Rongchen Guo, Takanori Fujiwara, Yiran Li, Kelly M. Lima, Soman Sen, Nam K. Tran, Kwan-Liu Ma
IEEE PacificVis 2020 Workshop on Visualization Meets AI, 2020
ArXiv Version Publisher's Version
Abstract
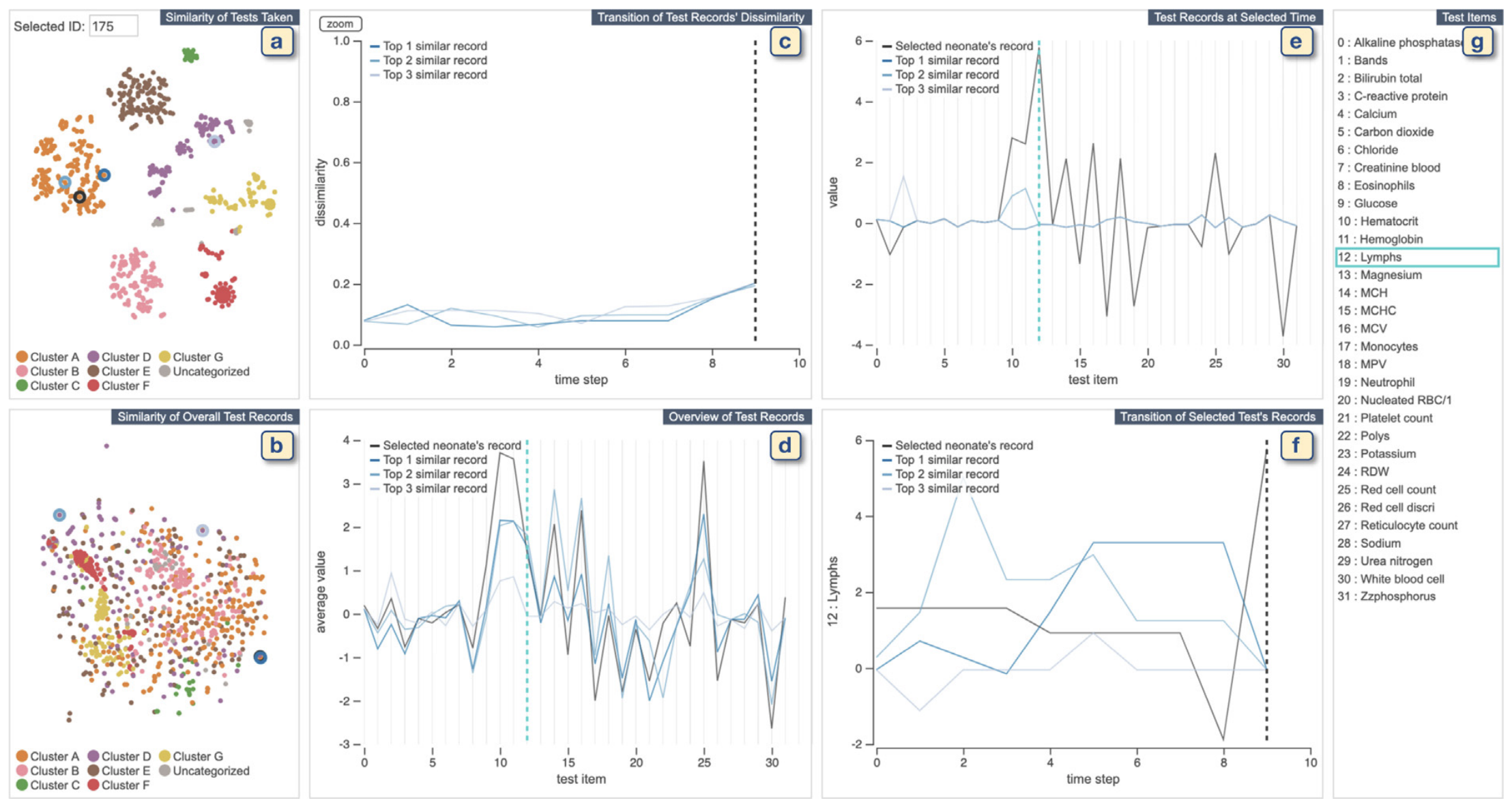
Machine learning for data-driven diagnosis has been actively studied in medicine to provide better healthcare. Supporting analysis of a patient cohort similar to a patient under treatment is a key task for clinicians to make decisions with high confidence. However, such analysis is not straightforward due to the characteristics of medical records: high dimensionality, irregularity in time, and sparsity. To address this challenge, we introduce a method for similarity calculation of medical records. Our method employs event and sequence embeddings. While we use an autoencoder for the event embedding, we apply its variant with the self-attention mechanism for the sequence embedding. Moreover, in order to better handle the irregularity of data, we enhance the self-attention mechanism with consideration of different time intervals. We have developed a visual analytics system to support comparative studies of patient records. To make a comparison of sequences with different lengths easier, our system incorporates a sequence alignment method. Through its interactive interface, the user can quickly identify patients of interest and conveniently review both the temporal and multivariate aspects of the patient records. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our design and system with case studies using a real-world dataset from the neonatal intensive care unit of UC Davis.
BibTex
@article{guo2020comparative,
title={Comparative visual analytics for assessing medical records with sequence embedding},
author={Guo, Rongchen and Fujiwara, Takanori and Li, Yiran and Lima, Kelly M and Sen, Soman and Tran, Nam K and Ma, Kwan-Liu},
journal={Visual Informatics},
volume={4},
number={2},
pages={72--85},
year={2020},
publisher={Elsevier}
}