Visual Analytics of Neuron Vulnerability to Adversarial Attacks on Convolutional Neural Networks
Yiran Li, Junpeng Wang, Takanori Fujiwara, and Kwan-Liu Ma
ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems, 2023
PDF ArXiv Version Publisher's Version
Abstract
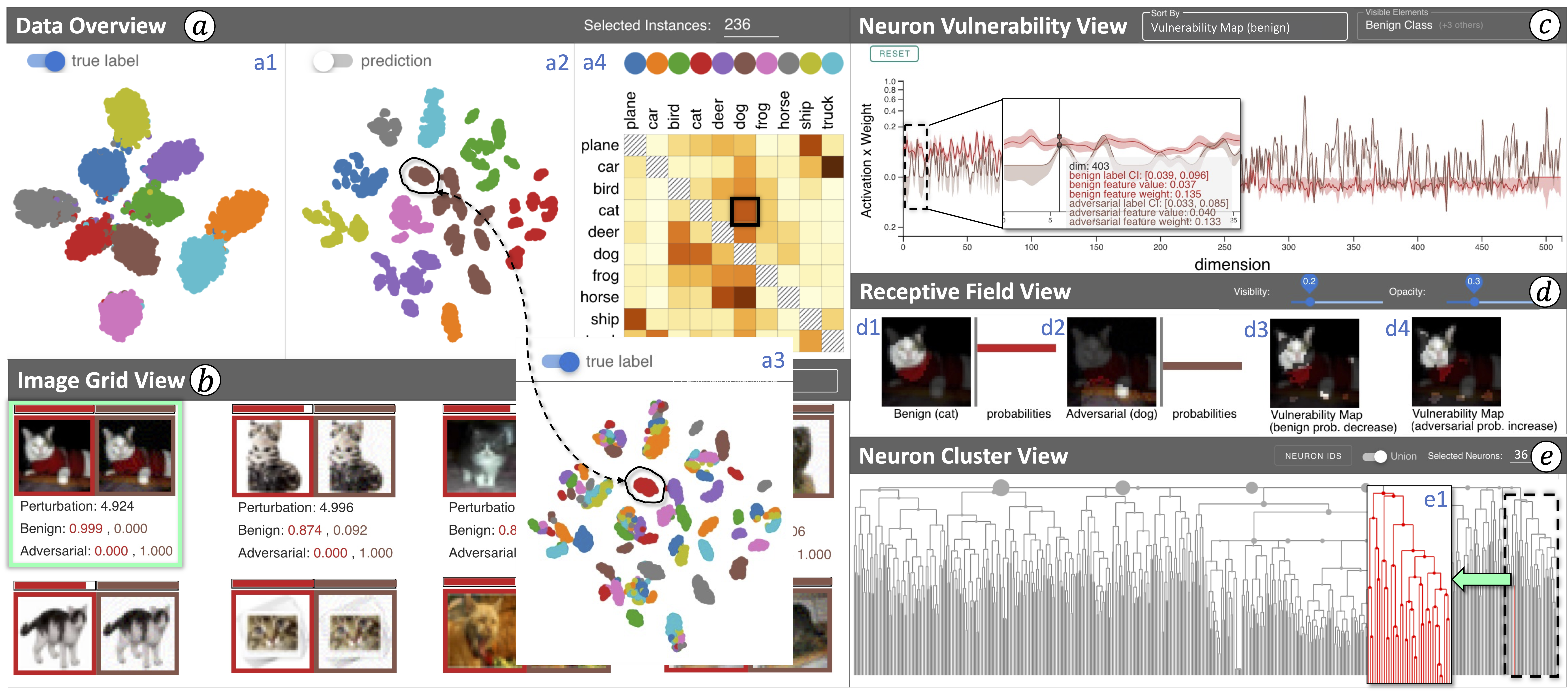
Adversarial attacks on a convolutional neural network (CNN)—injecting human-imperceptible perturbations into an input image—could fool a high-performance CNN into making incorrect predictions. The success of adversarial attacks raises serious concerns about the robustness of CNNs, and prevents them from being used in safety-critical applications, such as medical diagnosis and autonomous driving. Our work introduces a visual analytics approach to understanding adversarial attacks by answering two questions: (1) Which neurons are more vulnerable to attacks? and (2) Which image features do these vulnerable neurons capture during the prediction? For the first question, we introduce multiple perturbation-based measures to break down the attacking magnitude into individual CNN neurons and rank the neurons by their vulnerability levels. For the second, we identify image features (e.g., cat ears) that highly stimulate a user-selected neuron to augment and validate the neuron’s responsibility. Furthermore, we support an interactive exploration of a large number of neurons by aiding with hierarchical clustering based on the neurons’ roles in the prediction. To this end, a visual analytics system is designed to incorporate visual reasoning for interpreting adversarial attacks. We validate the effectiveness of our system through multiple case studies as well as feedback from domain experts.
BibTex
@article{li2023visual,
title={Visual Analytics of Neuron Vulnerability to Adversarial Attacks on Convolutional Neural Networks},
author={Li, Yiran and Wang, Junpeng and Fujiwara, Takanori and Ma, Kwan-Liu},
journal={ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems},
year={2023},
publisher={ACM New York, NY}
}